
By:
Arip Nurahman
Department of Physics
Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, Indonesia University of Education
and
Follower Open Course Ware at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Cambridge, USA
Department of Physics
http://web.mit.edu/physics/
http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Physics/index.htm
&
Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering
http://web.mit.edu/aeroastro/www/
http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Aeronautics-and-Astronautics/index.htm
Arip Nurahman
Department of Physics
Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, Indonesia University of Education
and
Follower Open Course Ware at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Cambridge, USA
Department of Physics
http://web.mit.edu/physics/
http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Physics/index.htm
&
Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering
http://web.mit.edu/aeroastro/www/
http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Aeronautics-and-Astronautics/index.htm


Vector Calculus
From Wikipedia
Vector calculus (also called vector analysis) is a field of mathematics concerned with multivariable real analysis of vectors in an inner product space of two or more dimensions (some results — those that involve the cross product — can only be applied to three dimensions). It consists of a suite of formulae and problem solving techniques very useful for engineering and physics. Vector analysis has its origin in quaternion analysis, and was formulated by the American engineer and scientist J. Willard Gibbs and the British engineer Oliver Heaviside.
Vector calculus is concerned with scalar fields, which associate a scalar to every point in space, and vector fields, which associate a vector to every point in space. For example, the temperature of a swimming pool is a scalar field: to each point we associate a scalar value of temperature. The water flow in the same pool is a vector field: to each point we associate a velocity vector.
Vector operations
Vector calculus studies various differential operators defined on scalar or vector fields, which are typically expressed in terms of the del operator
( ). The four most important operations in vector calculus are:
). The four most important operations in vector calculus are:| Operation | Notation | Description | Domain/Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gradient |  | Measures the rate and direction of change in a scalar field. | Maps scalar fields to vector fields. |
| Curl |  | Measures the tendency to rotate about a point in a vector field. | Maps vector fields to vector fields. |
| Divergence |  | Measures the magnitude of a source or sink at a given point in a vector field. | Maps vector fields to scalar fields. |
| Laplacian | 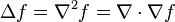 | A composition of the divergence and gradient operations. | Maps scalar fields to scalar fields. |
Theorems
Likewise, there are several important theorems related to these operators which generalize the fundamental theorem of calculus to higher dimensions:| Theorem | Statement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gradient theorem | 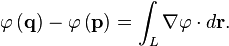 | The line integral through a gradient (vector) field equals the difference in its scalar field at the endpoints of the curve. |
| Green's theorem |  | The integral of the scalar curl of a vector field over some region in the plane equals the line integral of the vector field over the curve bounding the region. |
| Stokes' theorem | 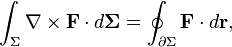 | The integral of the curl of a vector field over a surface equals the line integral of the vector field over the curve bounding the surface. |
| Divergence theorem | 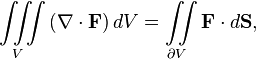 | The integral of the divergence of a vector field over some solid equals the integral of the flux through the surface bounding the solid. |
See also
- Vector calculus identities
- Irrotational vector field
- Solenoidal vector field
- Laplacian vector field
- Vector Analysis (Gibbs/Wilson)
References
- Michael J. Crowe (1994). A History of Vector Analysis : The Evolution of the Idea of a Vectorial System. Dover Publications; Reprint edition. ISBN 0-486-67910-1. (Summary)
- H. M. Schey (2005). Div Grad Curl and all that: An informal text on vector calculus. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-92516-1.
- J.E. Marsden (1976). Vecor Calculus. W. H. Freeman & Company. ISBN 0-7167-o462-5.
- Chen-To Tai (1995). A historical study of vector analysis. Technical Report RL 915, Radiation Laboratory, University of Michigan.
External links
- Expanding vector analysis to a non-orthogonal space
- Vector Analysis: A Text-book for the Use of Students of Mathematics and Physics, (based upon the lectures of Willard Gibbs) by Edwin Bidwell Wilson, published 1902.


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar